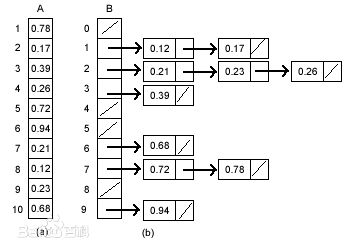
- 算法可视化:连接
- 时间复杂度,\(O(n+C)\),其中\(C=n \times (logn - logm)\)
- 空间复杂度,\(O(n+m)\)
- 是否稳定:稳定
算法思想
桶排序是一种十分高效稳定的算法,但是其使用场景比较受限。
场景
- 待排序列的值处于一个可枚举的范围内
- 待排序列所在的枚举范围不应太大
算法
- 根据映射函数将元素放入特定的桶中
- 对每个分别桶进行排序
实现
/**
* @param array 待排序序列
* @param min <= 最小值
* @param max >= 最大值
* @param bucketCount 桶的数量
*/
void sort(int[] array, int min, int max, int bucketCount) {
//最后一个桶号为 bucketCount 所以这里要 + 1
//比如 元素为 max 的桶
List<Integer>[] buckets = new List[bucketCount + 1];
//每个桶的容量
int cap = (max - min) / bucketCount;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
//当前元素到桶号的索引
int index = (array[i] - min) / cap;
if (buckets[index] == null) {
buckets[index] = new LinkedList<>();
}
buckets[index].add(array[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < buckets.length; i++) {
if (buckets[i] != null) {
//每个桶分别排序
Collections.sort(buckets[i]);
}
}
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < buckets.length; i++) {
if (buckets[i] != null) {
Iterator<Integer> iter = buckets[i].iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
array[index++] = iter.next();
}
}
}